@Configuration은 어떻게 빈을 등록하고, 싱글톤으로 관리할까?
어노테이션을 사용해서 빈을 생성하는 방법은 크게 두 가지가 있다.
@Configuration과@Bean을 사용해 빈 설정 정보 클래스 생성@Component와 이를 상속한@Repository,@Controller어노테이션등을 사용해 자바 컴포넌트 생성
@Configuration은 어떻게 빈을 등록하고, 싱글톤으로 관리하는지 알아보자!
@Configuration이란?
@Configuration은 빈을 등록할 수 있는 어노테이션 중 하나이다.
Spring 공식 문서에서는 다음과 같이 설명하고 있다.
Indicates that a class declares one or more
@Beanmethods and may be processed by the Spring container to generate bean definitions and service requests for those beans at runtime
@Configuration어노테이션을 사용하면, 하나 이상의@Bean이 붙은 메서드가 포함된 빈 설정용 클래스를 만들 수 있다.- 스프링 컨테이너는
@Bean이 붙은 메서드를 통해 빈을 생성한다.
@Configuration으로 어떻게 빈을 등록하는지 자세히 살펴보자!
@Configuration 사용 예시
// 빈으로 등록할 클래스
public class MyBean {
public void sayHello() {
System.out.println("안녕하세요, MyBean입니다.");
}
}@Configuration
public class Config {
@Bean
public MyBean myBean() {
return new MyBean();
}
}ApplicationContext는 @Configuration이 붙은 클래스 내부에서 @Bean이 붙은 메서드들을 찾는다.
@Bean이 붙은 메서드들은 자바 객체를 반환하는 메서드이다.- 반환된 자바 객체는 스프링 컨테이너에 빈으로 등록된다.
- 빈의 이름은
@Bean이 붙은 메서드 이름이 된다. (이 코드의 경우 메서드명과 같은myBean빈이 생성된다.)
등록한 빈 가져오기 - getBean()
앞서 말했듯이, ApplicationContext는 @Configuration 클래스가 정의한 빈에 대한 정보를 전부 읽어서 등록한다.
ApplicationContext의 getBean()메서드를 통해 빈에 대한 정보를 가져올 수 있다.
getBean()에 들어가는 인자는 다음과 같다.
getBean(빈의 이름, 빈의 타입);
getBean(빈의 이름)만으로도 빈을 가져올 수 있긴 하지만 Object 타입으로 반환되기 때문에 타입 변환이 필요하다. 빈의 타입을 안다면 명시해 주는 게 좋다.
getBean() 사용 예시
// getBean()을 사용해서 빈 객체를 불러올 수 있음
@SpringBootTest
public class ConfigTest {
@Autowired
ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Test
public void test(){
MyBean bean = applicationContext.getBean("myBean", MyBean.class);
bean.sayHello();
}
}// 실행 결과
안녕하세요, MyBean입니다.Configuration의 속성
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Configuration {
@AliasFor(annotation = Component.class)
String value() default "";
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
@Configuration에는 두 개의 속성이 존재한다. 속성 value는 @Configuration이 붙은 클래스가 빈으로 등록될 때의 이름을 설정할 수 있게 해준다.
우리가 이번에 자세히 알아볼 속성은 proxyBeanMethods이다. proxyBeanMethods는 @Configuration이 빈을 싱글톤으로 관리하는 것과 연관이 있는 속성이다. 아래에서 더 살펴보자!
proxyBeanMethods
빈에 대한 프록시 객��체를 생성할지 여부를 결정한다.
- 디폴트 값은 true이다. 즉, 디폴트로 빈에 대한 프록시 객체가 생성된다.
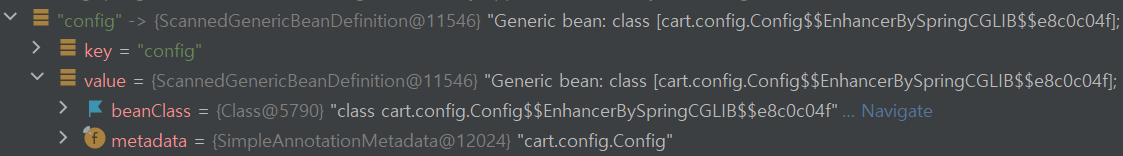
proxyBeanMethods = true일 때의 config빈의 상태
proxyBeanMethods = false일 때의 config빈의 상태
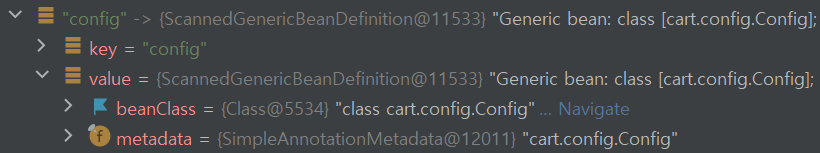
두 config의 차이가 보이는가? 프록시 객체로 생성한 빈의 클래스 이름을 보면 $$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB&& 라는 게 추가된 것을 알 수 있다.
CGLIB?
cglib is a powerful, high performance and quality Code Generation Library. It is used to extend Java classes and implements interfaces at runtime.
Byte Code Generation Library is high level API to generate and transform JAVA byte code. It is used by AOP, testing, data access frameworks to generate dynamic proxy objects and intercept field access.
바이트 코드를 가지고 프록시 객체를 만들어주는 라이브러리이다. ��런타임 시에 자바 클래스를 상속하고 인터페이스를 구현해 동적 프록시 객체를 만든다.
즉, proxyBeanMethods가 true인 상태에서 사용되는 config 빈은 우리가 직접 생성한 객체가 아니라 CGLIB 라이브러리에서 생성해 준 프록시 객체임을 의미한다.
왜 프록시 객체를 생성할까?
Spring 공식 문서 - Configuration : proxyBeanMethods
Specify whether
@Beanmethods should get proxied in order to enforce bean lifecycle behavior, e.g. to return shared singleton bean instances even in case of direct@Beanmethod calls in user code. This feature requires method interception, implemented through a runtime-generated CGLIB subclass which comes with limitations such as the configuration class and its methods not being allowed to declarefinal.
스프링은 싱글톤 타입인 빈을 만들기 위해 프록시 객체를 생성한다. CGLIB라이브러리를 사용해 Configuration 클래스를 그대로 사용하지 않고, Configuration을 상속한 프록시 객체를 새로 만든다고 한다.
아래는 그 예시이다.
@Configuration
public class Config { // 정의한 Configuration 클��래스
@Bean
public MyBean MyBean() {
return new MyBean();
}
}public class ConfigExt extends Config { // 실제로 빈을 반환하는 데 사용되는 클래스
private Map<String, Object> beans = ...;
@Override
public MyBean MyBean() {
if(!beans.containsKey("MyBean")) {
beans.put("MyBean", super.MyBean());
}
return (MyBean) beans.get("MyBean")
}
}물론 실제 코드는 이보다 더욱 복잡하다고 한다. 예시용으로 참고만 하자.
기존 클래스를 상속해야 하므로, Configuration은 final 클래스로 생성할 수 없다고 한다.
proxyBeanMethods 적용 예시
proxyBeanMethods = true 일 때
사용 예시를 위해 빈으로 등록할 세 개의 클래스를 생성했다. (BabyBean, MotherBean, FatherBean)
세 클래스는 모두 생성이 될 때, BabyBean을 출력한다.
public class BabyBean {
public BabyBean(){
System.out.println("애기 빈 : " + this);
}
}public class MotherBean {
public MotherBean(BabyBean babyBean) {
System.out.println("엄마 빈 : " + babyBean);
}
}public class FatherBean {
public FatherBean(BabyBean babyBean) {
System.out.println("아빠 빈 : " + babyBean);
}
}세 클래스를 @Configuration을 사용해 빈으로 등록해 보자.
@Configuration
public class Config {
@Bean
public BabyBean babyBean() {
return new BabyBean();
}
@Bean
public MotherBean motherBean() {
return new MotherBean(babyBean());
}
@Bean
public FatherBean fatherBean() {
return new FatherBean(babyBean());
}
}// 실행 결과
애기 빈 : com.example.controlleradvicetest.config.BabyBean@2d0566ba
엄마 빈 : com.example.controlleradvicetest.config.BabyBean@2d0566ba
아빠 빈 : com.example.controlleradvicetest.config.BabyBean@2d0566ba- 실행 결과를 보면,
FatherBean,MotherBean,BabyBean생성자로 출력된BabyBean객체가 전부 같은 것을 확인할 수 있다. - 이는
BabyBean객체는 한 번 생성된다는 것을 의미한다. (싱글톤)
proxyBeanMethods = false 일 때
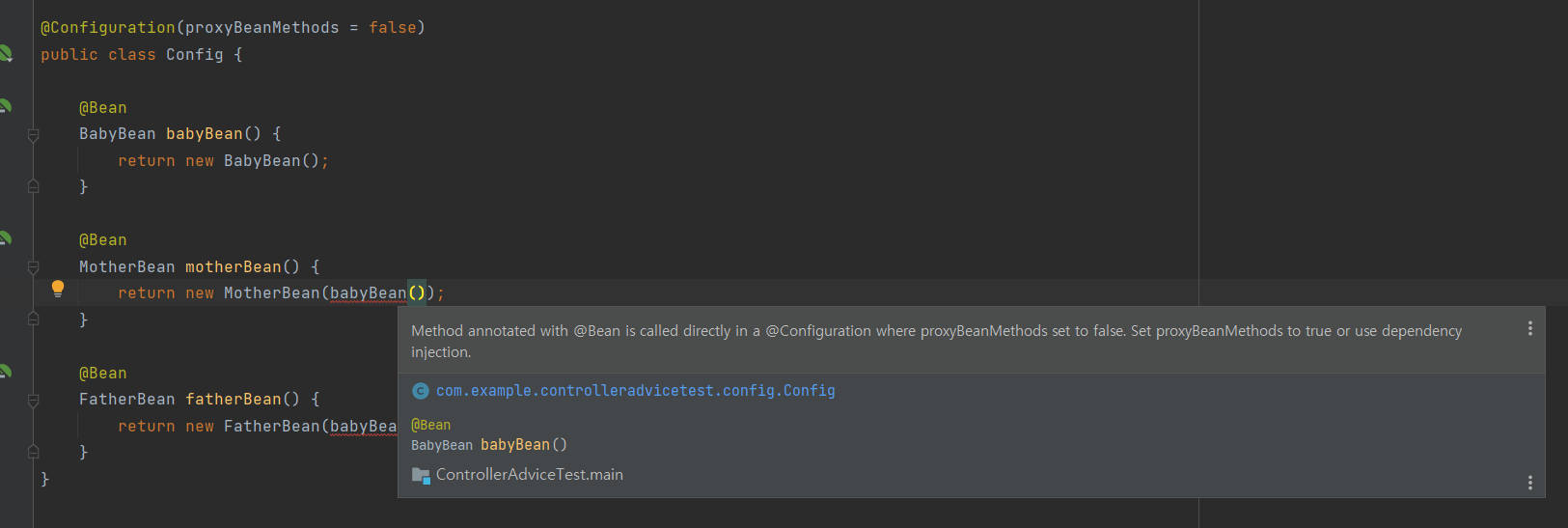
- 동일한
@Configuration클래스 내에서는proxyBeanMethod가 false 이면 아예 할당이 안 되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
@Cofiguration 클래스를 두 개로 분리해서 의존성을 주입해 주면 작동하지 않을까?
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) // babyBean 프록시 객체를 생성하지 않는 @Configuration 클래스
public class Config {
@Bean
public BabyBean babyBean() {
return new BabyBean();
}
}@Configuration
public class ParentConfig {
@Autowired
Config config; // babyBean을 생성하는 @Configuration 빈 객체를 주입받는다
@Bean
public MotherBean motherBean() {
return new MotherBean(config.babyBean()); // babyBean 주입
}
@Bean
public FatherBean fatherBean() {
return new FatherBean(config.babyBean()); // babyBean 주입
}
}
public class ConfigTest {
@Test
public void test(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class, ParentConfig.class);
BabyBean babyBean = context.getBean("babyBean", BabyBean.class);
System.out.println(babyBean);
MotherBean motherBean = context.getBean("motherBean", MotherBean.class);
FatherBean fatherBean = context.getBean("fatherBean", FatherBean.class);
}
}// 실행 결과
애기 빈 : com.example.controlleradvicetest.config.BabyBean@c8b96ec
애기 빈 : com.example.controlleradvicetest.config.BabyBean@2fa7ae9
엄마 빈 : com.example.controlleradvicetest.config.BabyBean@2fa7ae9
애기 빈 : com.example.controlleradvicetest.config.BabyBean@7577b641
아빠 빈 : com.example.controlleradvicetest.config.BabyBean@7577b641proxyBeanMethods = false로 설정하니,babyBean이 싱글톤으로 생성되지 않는 것을 볼 수 있다.motherBean과fatherBean에babyBean을 주입할 때,config에서 새로운babyBean객체를 생성해 주입해 주는 것을 알 수 있다.
@Configuration vs @Component
@Configuration은 내부적으로 @Component를 상속받고 있다.
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Configuration {
...
}@Component를 사용해서 원하는 클래스를 빈으로 등록할 수 있는데 @Configuration이 왜 필요한 걸까?
포인트는 @Component는 구현한 클래스 위에 선언해야 하지만, @Configuration은 @Bean이 붙은 메서드 내부에서 생성한 객체를 빈으로 등록할 수 있다는 점이다.
외부에서 구현한 클래스를 빈으로 등록하고 싶은데, 이 클래스가 read-only로 쓰였다면 @Component를 클래스 위에 선언할 수 없다. @Configuration을 사용하면, 메서드 내부에서 해당 클래스를 호출해 반환함으로써 빈으로 등록할 수 있다.
또, 하나의 클래스에서 빈들을 관리하고 싶거나, 특정 패키지 내부에 있는 빈들만 스프링 컨테이너에 등록하고 싶은 경우는 @Configuration을 사용하면 편리하게 관리할 수 있다.
마무리
@Configuration으로 빈을 등록하는 방법과 @Configuration이 빈을 싱글톤으로 관리하는 방법에 대해 알아보았다.
@Configuration은 @Bean이 붙은 메소드에서 호출한 객체를 빈으로 등록할 수 있기에 외부 라이브러리의 클래스도 빈으로 등록하는 것이 가능하다. 또한 @Configuration은 빈 객체를 프록시 객체로 만들어 싱글톤으로 관리한다는 것을 알 수 있었다.
여러 개의 빈을 함께 관리하고 싶을 때, 외부 라이브러리 등 개발자가 관리할 수 없는 클래스를 빈으로 등록하고 싶은 경우에는 @Configuration을 활용해 보도록 하자.
